Layer 2 network switches ensure fast and reliable data transfer in Local Area Networks (LANs) in current IT systems. These OSI model data link layer switches route data between devices using MAC addresses.
This makes the network faster and less crowded. Layer-2 switches, unlike traditional hubs, give data its own dedicated paths and boost bandwidth using layer 2 networking principles that are core to what is layer 2 in networking. This guide discusses what Layer-2 switches are and how they are used in the real world. It gives you a full picture of how important it is for improving network operations, especially in layer 2 connectivity, and answers the question: what is one function of a layer 2 switch?
Understanding Layer 2 in Blockchain: How It Works and Why It Matters
The goal of Layer 2 solutions in blockchain technology is to make it easier to scale and work more efficiently without affecting the security and transparency of Layer 1 solutions. These L2 networks, including layer 2 blockchains like Arbitrum One and Polygon, and platforms such as Zavros network are built on top of Layer 1. They make transfers faster and cheaper using off-chain transaction batching. This is how layer 2 blockchain works and why layer 2 blockchain is essential for Web3 evolution.
How It Works?
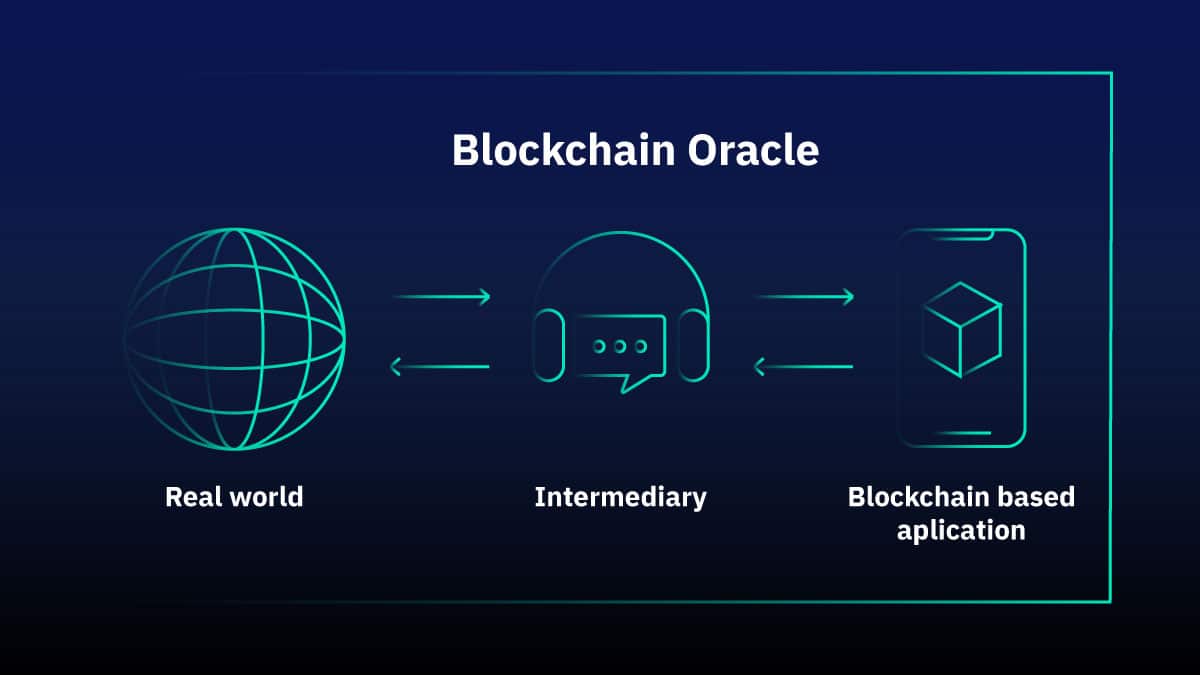
Layer 2 declutters and speeds up the main blockchain by moving transactions off. Token standards explained in rollup designs permit off-chain processing, which aggregates transactions before sending them back to the Layer 1 blockchain for approval. Blockchain oracles and oracle verification steps can also support Layer-2 final settlement logic.
This speeds things up and cuts expenses by taking the load off the main network. This is very important for expanding blockchain networks like Ethereum.
What It Matters?
Layer 2 solutions are very important for fixing blockchain’s scaling problems, especially when demand is high. These layer 2 blockchain protocols for crypto increase throughput without lowering blockchain integrity. L2 interoperability stacks like Zavros network sequencers, Validium, and Layer-2 ZK proof systems also benefit. Layer 2 handles more transactions off-chain, which greatly reduces delay and transaction fees.
This makes blockchain technology more useful and easy to use in real life. These options are necessary for a lot of people to use them, especially in finance, gaming, and supply chain management.
As more businesses work on Layer 2 protocols like state channels, rollups, and sidechains, blockchains may get better. Ethereum and other major blockchain platforms have started building Layer 2 solutions to speed up and improve their networks so they can handle millions of transactions per day.
Layer 2 vs. Layer 1: Key Differences Explained
Layer 1 and Layer 2 are key blockchain design concepts. Each contributes differently to the network. Both aim to improve blockchain technology’s efficiency and scalability, but for different reasons.
Layer 1: The Foundation of Blockchain
Base blockchain networks like Bitcoin and Ethereum are Layer 1. Transactions, consensus, and safety are its main duties. These networks can manage autonomous, open, and safe transactions, but as transactions expand, they may become crowded.
This slows speeds and raises prices, especially with several requests. Despite these issues, Layer 1 answers are crucial to blockchain integrity and trustworthiness.
Layer 2: Improving Scalability and Efficiency
Layer 2 solutions build on Layer 1 and offer scalability and better transaction efficiency by taking on a lot of the transaction work outside of the blockchain. These methods handle transactions off Layer 1 and settle them later. This reduces network congestion and transaction costs. Layer-2 solutions like rollups, sidechains, and state channels are popular because they increase speed and security.
Key Differences
Transaction Speed and Cost
- Layer 1: This first level of the blockchain handles transactions directly, which can lead to delays and higher transaction fees during busy times.
- Layer 2: Layer 2 solutions make deals faster and cheaper by processing them off-chain and then finalizing them on Layer 1. This makes them more scalable.
Data Handling
- Layer 1: Layer 1 stores all transactions and data on the blockchain. It slows and takes more energy.
- Layer 2: Handles most of the data off-chain and groups it together before sending it to Layer 1. This distributes the data load and boosts total efficiency.
Security
- Layer 1: Gets direct benefits from the main blockchain’s strong security model, which guarantees high stability and resistance to attacks.
- Layer 2: Builds on Layer 1’s security by adding extra features like proofs or fraud protection to keep transactions safe while they are being handled off-chain.
Scalability
- Layer 1: Limited by the blockchain’s built-in ability to handle transactions; often hits speed bumps during peak demand times.
- Layer 2: The purpose of Layer 2 is to increase capacity by taking over transaction handling from Layer 1. This lets the network handle more transactions without slowing down.
Use Cases
- Layer 1: This is for smart contracts and decentralized apps (dApps) that need to connect to the main blockchain directly.
- Layer 2: Best for applications that need to handle transactions quickly, like gaming, high-frequency trading, and microtransactions.
Core Features and Benefits of Layer 2 Networks
Layer 2 networks greatly improve speed, scalability, and cost-effectiveness, making them a strong choice for blockchain and network systems that are in high demand. Layer 2 speeds things up without lowering security by taking transfers off of the main blockchain. All of these things are good:
Increased Speed
Off-chain processing cuts down on delays and speeds up transactions, which is important for DeFi, games, and NFT platforms.
Scalability
Layer 2 networks can handle a lot of transactions without putting too much stress on Layer 1. They offer high throughput and allow decentralized apps (dApps) to grow while keeping Layer 1’s security.
Cost Efficiency
Layer 2 lowers transaction fees by making the base blockchain less busy. This makes it a cheaper choice for regular or small transactions.
Improved User Experience
Layer 2 solutions make the experience smoother by completing transactions faster and lowering wait times. This makes sure that people can connect in real time on decentralized platforms.
Environmental Impact
Layer 2 is better for the environment than Layer 1 because it uses less energy because it combines off-chain activities into a single proof.
Future-Proof Flexibility
Layer 2’s flexibility lets new ideas keep coming up without making big changes to the base blockchain. This guarantees long-term growth and stability.
Popular Layer 2 Solutions and Real-World Examples
Layer 2 solutions scale Layer 1 blockchains, boosting transaction speed, cost, and network efficiency while retaining security. What are the most popular Layer 2 options and how do they work?
- Arbitrum: To make Ethereum more scalable, Arbitrum uses rollups to handle transactions off-chain and lower delays. Arbitrum Nova is designed for very low-cost, fast applications like gaming and social media. Arbitrum One, on the other hand, supports DeFi projects, which increases the speed and efficiency of transactions.
- Polygon (previously Matic): Polygon is a way to make Ethereum more scalable by combining the Plasma and PoS sidechains. A lot of dApps, DeFi, and NFT platforms use it because it has lower fees and faster transaction speeds than Ethereum’s mainnet.
- zkSync and StarkWare: These zk-Rollup solutions make Ethereum more scalable by processing transactions off-chain and adding cryptographic proofs to keep them safe. Instead of focusing on specific smart contracts, zkSync offers fast, safe, and inexpensive transactions for trading applications.
- Optimism: This method lowers Ethereum transaction times and fees by assuming that transactions are valid until proven otherwise. Mostly used in DeFi apps, it runs faster and costs less than Ethereum’s base layer.
- Gnosis Chain: Gnosis has a sidechain solution that uses the DAI stablecoin to keep transaction costs stable. It helps a lot in DeFi and prediction markets, where knowing fees ahead of time and quickly confirming transactions are very important.
Layer 2 solutions have changed many fields, like DeFi, gaming, and NFTs, by making infrastructure more flexible, cheaper, and faster. These solutions are very important for getting more people to use blockchain and making decentralized apps work better.
Advanced Use Cases of Layer 2 Technology
Layer 2 technology is a powerful way to improve performance across many industries and make blockchain more scalable. Layer 2 is having a big effect in the real world because it speeds up transactions, lowers fees, and makes things run more smoothly.
Corporate Networks
Corporate networks often use Layer 2 switches to link workstations, printers, and servers in the same building. Virtual Local Area Networks (VLANs) divide network traffic into groups based on department, like HR, IT, and Finance. This makes the network safer, faster, and easier to handle.
Home Networks
In home offices or gaming setups, Layer 2 switches enable seamless communication between devices like laptops, Network Attached Storage (NAS), and media servers. These switches ensure efficient data handling within smaller, localized networks.
Data Centers
Data centers harness Layer 2 ethernet switches to manage high-volume traffic between server racks. Because they have low delay and make communication smooth, these switches are necessary for handling large amounts of data quickly.
Decentralized Finance (DeFi) at Retail Scale
Zk-Rollups, which enable high-frequency trading on platforms like dYdX and GMX, are transforming DeFi by lowering transaction costs and improving scalability without compromising security.
On-Chain Gaming
Game creators may mint in-game assets on zkEVM without hefty crypto gas fees using layer 2 technology like Immutable’s Passport wallet, increasing gameplay by making transactions faster and cheaper.
Micropayments and Remittances
Layer 2 enables cost-effective micropayments and cross-border remittances by offering faster transaction finality and lower fees, especially beneficial for stablecoins and everyday payments.
Blockchain Scalability in Real-Time Applications
Blockchain networks scale better with Layer 2 protocols, making them better for real-time applications like IoT and financial services that need low-latency, high-frequency transactions.
How Layer 2 Improves Speed, Scalability, and Efficiency
Layer 2 options make blockchain transactions go faster, make the network bigger, and make it work better. Layer 2 networks speed up transactions while keeping the foundation blockchain safe and decentralized. They are built on top of Layer 1 blockchains like Ethereum. How Layer 2 technology makes things go faster:
Enhanced Transaction Speed and Efficiency
Layer 2 networks handle transactions off-chain, greatly reducing congestion on Layer 1. This makes transaction confirmations happen faster and lets more transactions go through. Layer 2 solutions speed up data transfers by reducing activity on the chain. This makes them perfect for apps that need to do a lot of transactions in real time.
Scalability Improvements
Layer 2 options take some of the transaction load off of Layer 1 so that blockchains can grow more efficiently. Layer 2 makes the blockchain more scalable by letting it handle more transactions per second (TPS). This makes dApps easier to use for a lot more people because they can handle more users without being slower.
Cost Efficiency
Off-chain transactions and batching make Layer 2’s transaction fees lower than Layer 1’s. This cost cut is highly important because every transaction counts on microtransactions and DeFi systems. Lower Layer 2 costs make it easier for businesses and customers to use blockchain technology, which leads to more people using it.
Instant and Reduced-Confirmation Transactions
State channels and other Layer 2 off-chain approaches make it possible to do transactions almost instantly without the need for blockchain finality. In real-time services like games, micropayments, and interactive apps, this speeds things up.
Optimized Resource Utilization
Layer 2 also makes the best use of resources by making the base blockchain less busy. Along with keeping the main chain safe, this makes better use of blockchain resources like storage space and computing power.
Security and Reliability Considerations in Layer 2 Networks
Layer 2 (L2) networks are quicker and cheaper than Layer 1 (G) networks, but they also bring security threats that need to be addressed with. Here are the main worries about safety and dependability:
Bridge Risks
Using smart contract links to transport assets between Layer 1 (L1) and Layer 2 has been a problem in the past. The safety of these bridges is very important, because holes in them can cause big financial losses.
Centralization Risks
A lot of Layer 2 options, like rollups, still depend on centralized ways to upgrade or sequencers. This can be dangerous if the major organizations are hacked or if they work in a centralized way, which would defeat the purpose of decentralization. Byzantine fault tolerance is often replaced with the honest-majority assumption, which adds to the security risks of the network.
Data Availability Concerns
Validium and Optimistic Rollups are two Layer 2 designs that post cryptographic proofs on the blockchain but store raw data off the blockchain. With this method, they depend on outside data providers to keep info available. You might have trouble verifying transactions and keeping your info safe if these providers fail.
Best Practices
Use Layer 2 solutions with open-source node software, decentralized proposers, and fraud-proof systems that do not need authorization to lower these risks. These features improve security and openness, which helps make sure that Layer 2 networks stay trustworthy for users.
Current Challenges in Layer 2 Adoption
There are some problems with Layer 2 usage that make it hard to use by many people. The complicated user experience is a big problem. Things like bridging assets, switching RPCs, and handling gas tokens can be hard for newcomers to understand, which makes it harder for them to join.
Making these steps easier is important for making Layer 2 more approachable. There are also different versions of standards. There are wallet standards like EIP-4337 (account abstraction), but different platforms do not always use them the same way. This makes it hard for both users and developers to integrate. Another problem is that cross-chain links used in Layer 2 solutions are getting more and more attention from regulators, mostly because of worries about money laundering.
This increased governmental pressure could cause compliance costs to rise, which would slow down adoption. Lastly, there is a big gap in what is known. A lot of users and writers do not fully understand what Layer 2 does and how it works. We need more training programs to close this gap and get more people to use Layer 2 technology.
The Future of Layer 2 and Its Role in Web3 Evolution
Layer 2 solutions are important for the growth of Web3. They let Ethereum act as a settlement layer while Layer 2 takes care of everyday activities. Cross-rollup interactions will soon be possible on Optimism’s Superchain, and ZK-proof hardware claims transaction fees of less than a cent.
Scaling Layer 2 horizontally is the way of the future, whether it is through a single dominant rollup or multiple specialized Layer 2 networks. This will help the autonomous economy grow faster, more easily, and more cheaply.
Glossary: Key Terms in Layer 2 Networking
- MAC Address: This is the Media Access Control address: A number that is unique to a network interface card (NIC) and is used for network transmission.
- VLAN (Virtual LAN): A logical part of a network that lets devices talk to each other as if they were on the same real LAN, even if they aren’t.
- Collision Domain: A part of a network where data bits might bump into each other. Layer 2 switches separate data to different ports, which helps make collision domains smaller.
- LAN (Local Area Network): A network that only works in a small area, like an office, building, or home, and lets people talk to each other in that area.
- Layer 3 Switch: A device that works at the network layer of the OSI model and sends data based on IP addresses.
- Frame Forwarding: The use of MAC codes to send data frames from one device on the same network to another.
FAQs
How Does Ethereum’s Dencun Upgrade and EIP-4844 Impact Layer-2 Transaction Costs?
The Ethereum Dencun upgrade, especially EIP-4844 (Proto-Danksharding), lowers Layer-2 transaction costs by a lot. It does this by adding “blobs,” which are large pieces of data that are cheaper to keep on the blockchain than regular transaction data.
There is less need to use expensive Ethereum block rooms because these blobs can hold data that Layer-2 rollups need. Because of this, Layer-2 networks have lower fees and can grow more easily, which makes transfers cheaper for users.
Why Do Blobs Reduce the Cost of Rollup Transactions?
When you separate transaction data from the Ethereum mainnet and handle it off-chain, at a lower cost, blobs lower the cost of rollup transactions. Instead of storing each transaction’s data directly on the Ethereum blockchain, blobs combine many data points into one. This makes the Ethereum mainnet’s storage easier and lowers the overall cost of transactions for Layer-2 rollups.
Can EIP-4844 Make Ethereum Transactions Faster?
The main goal of EIP-4844 is to lower processing costs, not to directly speed things up. It indirectly speeds up Ethereum dApp transaction times by reducing costs and improving Layer-2 solutions. Layer-2 processing that is faster and cheaper can make the whole experience more efficient, which can increase the number of transactions.
What Are Layer-2 Networks?
It is possible to build secondary frameworks on top of current blockchains (Layer 1) to make them more scalable, lower transaction fees, and work better overall. Off-chain transaction processing and final transaction data settlement on the main blockchain reduce congestion and enable faster, cheaper transactions. Rollups, state routes, and sidechains are some examples.
How Do Layer-2 Networks Increase Transaction Speed?
Layer-2 networks speed up transactions by processing most of them off-chain. This makes the main blockchain (Layer-1) less busy. Layer-2 solutions group together several transactions before closing them on the main chain. This speeds up confirmation times. In this way, they reduce congestion and improve efficiency.
What Is the Ethereum Dencun Upgrade?
The Ethereum Dencun upgrade, which includes EIP-4844, introduces “proto-danksharding.” This upgrade boosts data throughput and lowers transaction costs for Layer-2 solutions by implementing blob-carrying capabilities.
Can I Use My Ethereum Wallet on Layer-2 Networks?
Yes, you can use your Ethereum wallet on Layer-2 networks. You can use Ethereum wallets with Layer-2 solutions, which means you can connect with Layer-2 apps and move assets between Layer-1 and Layer-2 networks. A lot of Layer-2 options work with Ethereum wallets, which makes it easy to connect the two networks.
What Is the Best Layer-2 Solution Right Now?
The best Layer-2 solution is different for each use case, but Optimism and Arbitrum are two common choices. They both use rollups to make them more scalable. Another widely used option is Polygon, which works with many dApps and lets you make transactions quickly.
More and more people are using zkSync and StarkWare (ZK-Rollups) because they focus on making things safer and more scalable. Because each option has its own features that work best with different kinds of apps, picking the best one for your project will depend on those needs.
What are layer 2 network devices?
LAN switches, bridges, MAC routers; Blockchain rollups, oracles, sidechains in crypto ecosystems.