The Role of Oracles in Decentralized Finance (DeFi)
Decentralized Finance, or DeFi, is a big change in financial services. It lets people lend, exchange, borrow, and do other financial activities on blockchain networks through smart contracts on blockchain, which do not need banks, brokers, or other common middlemen. But blockchains are closed systems by nature, so they can not get data from the real world directly. This limitation raises a common question: what is an oracle in blockchain and why is it needed?
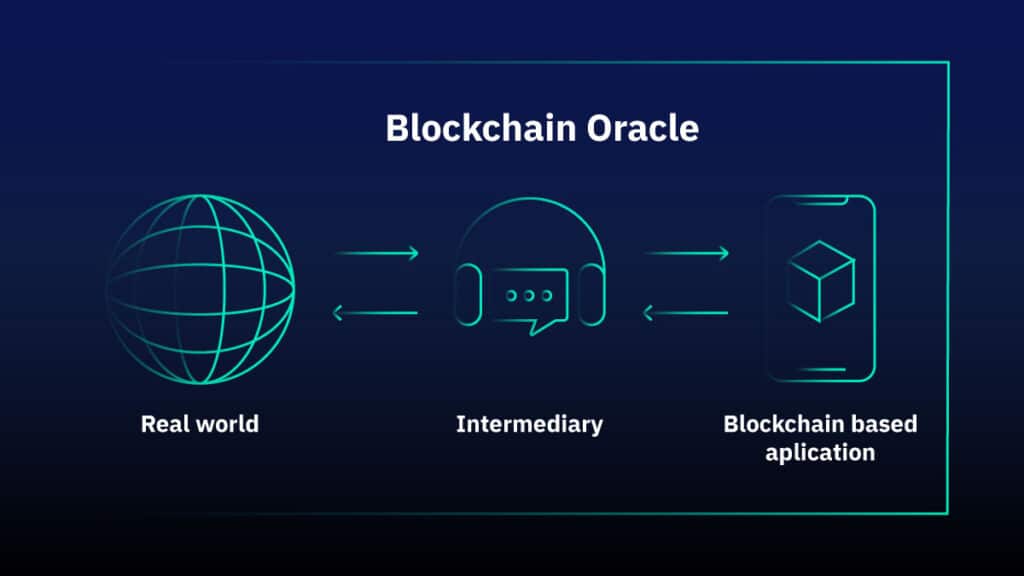
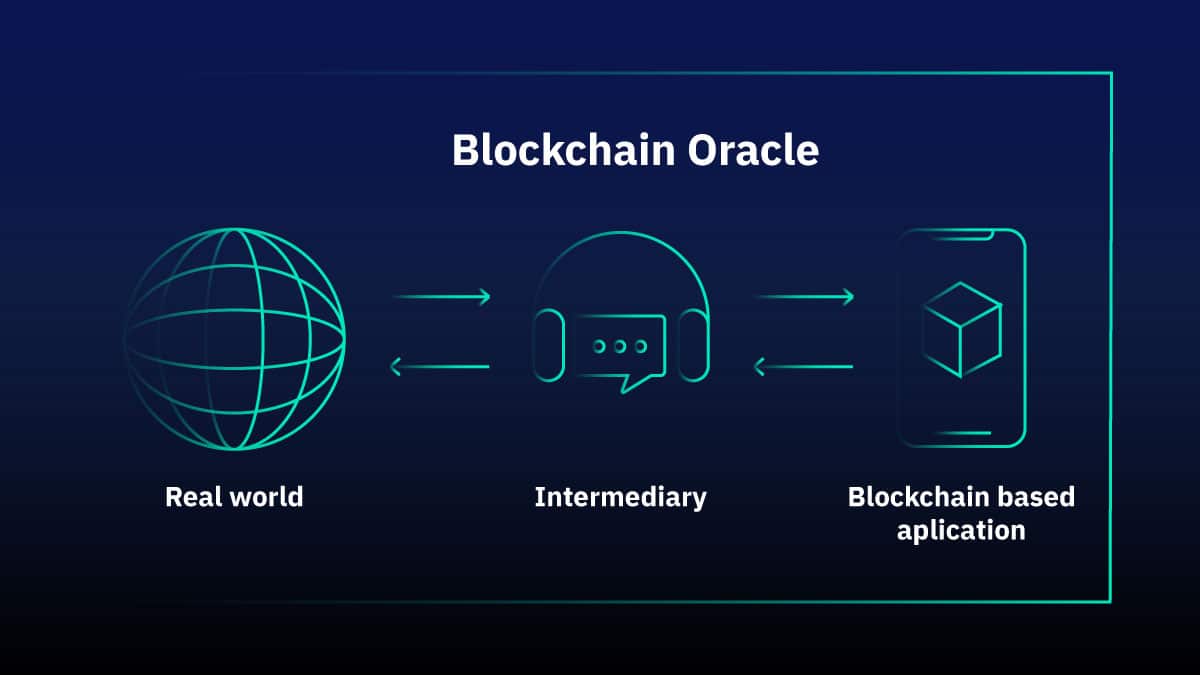
Without blockchain oracles, this constraint would significantly limit DeFi’s potential. The Role of Oracles in Blockchain & DeFi is to act as a trusted bridge between on-chain and off-chain environments.
DeFi relies heavily on oracles to work. They get real-world data like asset prices, market factors, and weather events, check it for accuracy, and send it straight to smart contracts. This allows smart contracts to execute on their own when conditions based on events in the real world are met. This makes DeFi apps dynamic and responsive, which lets them handle complicated financial products.
Oracles solve a major problem for decentralized systems: getting accurate, safe, and trusted off-chain data on-chain so DeFi platforms may run reliably and at scale. Without this important link, smart contracts would be cut off from the outside world, which would limit DeFi to static internal data and stop new ideas from being made.
What Are Blockchain Oracles and Why They Matter in DeFi
Many newcomers ask what is a blockchain oracle, what is an oracle, or what is an oracle in crypto. Blockchain oracles are specialized infrastructure services that let autonomous networks connect with systems and data sources that are outside of the network.
Smart contracts cannot access market prices, weather data, or event outcomes, unlike blockchains, which are immutable and isolated. In order to fill this gap, oracles get, check, and send off-chain data to on-chain apps. They work as a safe link between the outside world and blockchain systems.
Oracles are essential in Decentralized Finance (DeFi) since most financial applications need real-time external data. Lending and borrowing services need precise asset price feeds to determine collateral values, and algorithmic stablecoins need reliable price signals to maintain pegs. Without trustworthy oracle crypto systems, DeFi applications would be exposed to manipulation and failure.
In DeFi, blockchains oracles’ main job is to let smart contracts do more things by letting them run based on real-world events. This integration makes financial operations automated, open, and trust-free.
Examples include automated settlements in lending protocols and decentralized derivatives or insurance products. Oracles make decentralized finance useful in the real world, making it a strong replacement for standard systems of finance.
How DeFi Oracles Work: Connecting Smart Contracts With Real-World Data
To fully understand what are oracles in blockchain, it is important to know how they operate. DeFi oracles reconnect blockchains to the outside world. In order to stay safe, smart contracts can not directly access market prices, sports scores, weather, economic statistics, or other data that is stored off-chain. When smart contracts run logic, oracles gather, check, and send real-world data to them so that they can use correct external inputs.
Input and Output Data Flow
The oracle method usually goes through a defined cycle:
- Smart contracts request certain external data.
- The Oracle gathers needed data from reputable sources.
- Verify and combine data to eliminate errors or manipulation.
- The Oracle provides the final result on-chain.
- The smart contract performs based on data received.
Oracles give you up-to-date data that you can not change. This lets you use price feeds, automatic liquidations, insurance claims, prediction markets, and messaging cross-chain.
Oracle Architectures
Different oracle designs combine decentralization, security, and efficiency:
- Centralized oracles: Run by one organization or data source. They are easy and quick, but they have a single point of failure and need more trust.
- Decentralized crypto oracles: Use several data sources and nodes that are not connected to each other, and then use agreement to combine the results. This lowers the risk of being manipulated and raises reliability, which is common in big DeFi price feeds.
- Hybrid oracles: When you combine on-chain and off-chain parts, it lets you do complicated calculations, handle data privately, and work with both older systems and APIs.
Security and Trust Mechanisms
To be reliable, today’s oracles blockchain networks use a number of safety measures:
- cryptographic signatures and proofs
- node reputation and staking incentives
- economic consequences for dishonesty
- multi-source grouping and redundancy
- Some systems have secure enclaves and trusted execution environments.
Some oracle chains also use secure hardware environments. These mechanisms help protect against attacks that try to change data, cause downtime, or manipulate oracles. These attacks have previously caused big losses in DeFi when poorly secured oracles were used.
Why Oracles Are Essential for Secure and Reliable DeFi Systems
Smart contracts in decentralized finance (DeFi) require dependable real-world data links to work and stay safe. Oracles enable blockchains to securely receive, verify, and transmit external data. Oracle-less smart contracts using internal blockchain data would limit DeFi functionality and innovation.
Empowering Smart Contracts with Real-World Data
Smart contracts self-execute based on predefined circumstances. But blockchains can not get info from external sources on their own. Oracles analyze inputs including real-time price feeds, interest rates, weather data, and sports results to enable DeFi protocols to execute loan liquidations, automated trades, and insurance payouts reliably and autonomously.
Ensuring Trust and Decentralization
Two important things that blockchain technology is based on are security and freedom. Oracles improve these ideas by getting data from a lot of different sources and using decentralized validation methods.
This minimizes manipulation, single points of failure, and erroneous reporting by reducing data source dependence. Consensus and cryptographic proofs ensure data integrity before smart contract delivery in leading oracle systems like DONs.
Supporting Advanced DeFi Ecosystems
A lot of complex financial tasks are done by modern DeFi systems that depend on oracles. Examples:
- Loans and borrowing: Accurate pricing oracles avoid under-collateralization and ensure fair liquidations.
- Derivatives and synthetic assets: Trustworthy external information makes it possible to settle and price derivatives.
- Prediction Markets: Trusted off-chain sources must check the results of the events.
- Insurance Rules: Claims can only be made when situations in the real world prove that they are true.
By offering safe and reliable data feeds, oracles make new kinds of financial automation and innovation possible that would not be possible in fully decentralized environments.
Mitigating Risk Through Secure Architecture
Modern Oracle solutions have many security mechanisms to maintain reliability:
- multi-source data aggregation
- cryptographic verification
- reputation systems and economic incentives
- redundancy and fallback mechanisms
These steps keep DeFi systems safe from common threats like data hacking, oracle downtime, and misreporting. This helps keep financial operations honest and strong.
Different Types of Oracles in Blockchain Networks
Blockchain oracles can be different based on what kind of data they work with, how they deliver it, and how they are set up. Each type is made to meet the needs of a certain application while also combining speed, security, and decentralization.
1. Pull-Based Oracles (Data Feeds)
Pull-based oracles only get data from external sources when a smart contract tells them to. DeFi price feeds, which demand real-time asset prices, FX rates, and market indications before trading or liquidating, use them extensively.
2. Push-Based Oracles (Event-Driven Oracles)
Push-based oracles will automatically send data on-chain when certain things happen off-chain. When weather occurrences, shipment scans, or sensor data require fast response, insurance, logistics, and IoT systems use them.
3. Cross-Chain Oracles
Oracles that work cross chains let different blockchains connect to each other. These oracles support data and asset transfer across networks, addressing on chain vs off chain interoperability challenges, which helps with things like:
- multi-chain DeFi strategies
- asset bridging
- cross-chain governance
4. Compute-Enabled Oracles
Oracles that use computers to do calculations work off-chain, which means that the calculations are done outside of the blockchain. They only send the blockchain approved results. They are used for processes that would be too costly or impractical to run on blockchains directly, such as:
- zero-knowledge proofs.
- privacy-preserving data processing
- secure randomness generation (VRF)
- complex data aggregation
These oracles add new functionality to smart contracts while still allowing decentralization to work.
5. Centralized and Decentralized Oracles
Centralized oracles depend on just one data source. They work well, but they create the risk of a single point of failure.
Decentralized oracle networks (DONs) get information from a number of different nodes and combine the results through agreement. This makes the network much more secure and reliable.
Understanding the Oracle Problem and Its Solutions
Blockchains can not get info from external (off-chain) sources directly. So, smart contracts rely on “oracles,” but if an oracle gives data that is wrong or has been changed, the whole contract runs the wrong way. This difference in confidence is called the “oracle problem.”
Why The Oracle Problem is Important?
- blockchains are safe but isolated
- real-world info is external and usually centralized
- incorrect oracle data can lead to mistakes in liquidation, price attacks, and losing money.
Linking blockchains to real-world data without reestablishing authority is difficult.
Key Solutions Used Today
- Decentralized Oracle networks: several nodes get data and check it before placing it on-chain.
- Multi-source aggregation: feeds with different prices or events are combined, which lowers the risk of cheating.
- Cryptographic proofs and reliable hardware: make sure that data stays intact from the source to the blockchain.
- Staking and reducing rewards: punish oracle operators who are not honest
- Mixed smart contracts: on-chain logic with off-chain data processing that is safe
Solving the oracle problem lets DeFi applications employ accurate, tamper-resistant real-world data for safe lending, derivatives, insurance, identity, gaming, and IoT automation.
Key Takeaways: How Oracles Shape the Next Generation of DeFi
Oracles link blockchains to real-world data. Credit, derivatives, stablecoins, insurance, and real-world asset markets can use smart contracts. The next phase of DeFi will leverage safe, decentralized oracle networks to reduce manipulation risks, eliminate single points of failure, and enable cross-chain data sharing.
As ecosystems like Zavros Network expand, oracle systems will work closely with validators, making it essential to understand how validator nodes work. Better oracle design means safer protocols, higher user confidence, and a more scalable, interconnected decentralized finance.